PEO-131・301・302
PEROXIDASE from Horseradish

PREPARATION and SPECIFICATION
PEO-301/302 are isolated from horseradish root in our own method. PEO-131 is chromatographically separated from the other isoenzymes using SP Sephadex C-50 by the modified method of Paul et al.1) The peroxidase fractions having equal RZ values (ca.3.3) are combined to generate the preparation. This preparation has an RZ value of ca.3.3 and is electrophoretically homogeneous. On the other hand, GradeIII is partially purified preparation.
| Appearance | Reddish-brown amorphous powder, lyophilized | |
|---|---|---|
| Activity | GradeⅠ 250 Purpurogallin U/mg-solid or more
(-131) (RZ ≥ 3.0, salt free) GradeⅢ 110 Purpurogallin U/mg-solid or more (-301) (RZ ≥ 2.0, containing approx. 30% of stabilizers) GradeⅢ 180 Purpurogallin U/mg-solid or more (-302) (RZ ≥ 2.0, salt free) |
|
| Contaminant | Phosphatase ≤1.0×10-3 % (GradeIII) | |
PROPERTIES
| Stability | Stable at −20℃ for at least one year (Fig.1,2,3) |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | approx. 40,000 |
| Structure | Glycoprotein with one mole of protohaeminIX 2) |
| Inhibitors | Cyanide, sulfide, fluoride, azide 3) |
| Optimum pH | 6.0−7.0 (Fig.6) |
| Optimum temperature | 45℃ (Fig.7) |
| pH Stability | pH 5.0−10.0 (25℃, 20hr) (Fig.8) |
| Thermal stability | below 50℃ (pH 6.0, 10min) (Fig.9) |
| Effect of various chemicals | (Table 1) |
APPLICATIONS 4〜11)
This enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of H2O2 in clinical analysis. Especially, the highly purified preparation (Grade I) is useful as a protein tracer in histo-and cyto-chemistry and as a valuable experimental tool in hodological neurography. Also, the enzyme preparation has been used as an enzyme label in enzyme immunoassay. Grade III(-302) is suitable for dry chemistry. On the other hand, the enzymes contribute for the reduction of phehol in waste water.
ASSAY
Principle

The appearance of Purpurogallin is measured at 405nm by spectrophotometry.
Unit definition
One purpurogallin unit causes the formation of one milligram of purpurogallin in 20 seconds at 20°C and pH6.0.
Multiply the measured results in following method by the factor and convert to the units defined above.
Method
Reagents
- Buffer solution for dilution of hydrogen peroxide:
50 mM phosphate buffer pH 6.4, containing 0.01% Triton X-100 - 13.5 mM hydrogen peroxide solution (Should be prepared fresh)
Add 0.459 ml of 30% (W/V) hydrogen peroxide solution to 300 ml of solution (A). - 7.8%(W/V) Pyrogallol solution (Should be prepared fresh)
- Buffer solution for enzyme dissolution and dilution:
0.1M phosphate buffer solution pH 6.0, containing 0.01% Triton X-100.
Enzyme sample:
Dilute the enzyme sample to 0.14-0.28 U/ml with ice-cold solution (D) immediately before analysis.
Procedure
1.Prewarming the bottle containing solution (C) at 37°C.
2.Prepare the following reaction mixture in a test tube and prewarm at 37℃ for about 3minutes
| 4ml | Solution (B) |
|---|---|
| 0.2ml | Enzyme solution |
3.After prewarming the reaction mixture, add 1.0 ml of solution (C) to the reaction mixture and stir, then pour into a cuvette (d = 1.0 cm)
and set on a spectrophotometer controlled at 37°C.
against water.
4.Measure absorbance at 405 nm 30 seconds and 90 seconds after the addition of solution (C).
ΔODtest=OD(90 seconds)−OD(30 seconds)
At the same time, measure the blank(ΔODblank) by using the same method as the test except that Solution
(D) is added instead of Enzyme solution.
ΔODblank=OD(90 seconds)−OD(30 seconds)
Calculation
Activity* can be calculated by using the following formula.
Volume activity(U/ml) = (ΔODtest−ΔODblank) × 0.473 × df
Weight activity(U/mg) = (U/ml) × 1/C
| 0.473 | : Conversion factor to Purpurogallin units (U) of the above definition |
| C | : Enzyme concentration in dissolution (c mg/ml) |
| *One purpurogallin unit is equivalent to 13.5 international units determined with o-dianisidine at 25℃ | |
REFERENCES
Table 1. Effect of Various Chemicals on Peroxidase
[The enzyme dissolved in 0.1M phosphate buffer, pH 6.0 (50U/ml) was incubated with each chemical at 25℃ for 1hr.]
-
Chemical Concn.(mM) ※Residual
activity(%)None - 100 Metal salt 2.0 MgCl2 102 CaCl2 102 Ba(OAc)2 105 FeCl3 98 CoCl2 97 MnCl2 97 ZnCl2 99 CdCl2 99 NiCl2 96 CuSO4 98 Pb(OAc)2 96 AgNO3 91 HgCl2 92 2-Mercaptoethanol 2.0 94 PCMB 1.0 98 -
Chemical Concn.(mM) ※Residual
activity(%)MIA 2.0 99 NEM 2.0 97 IAA 2.0 99 Hydroxylamine 2.0 98 EDTA 5.0 95 o-Phenanthroline 2.0 98 α,α′-Dipyridyl 1.0 96 Borate 50 98 NaF 2.0 98 NaN3 2.0 75 Triton X-100 0.10% 98 Brij 35 0.10% 80 Tween 20 0.10% 89 Span 20 0.10% 98 Na-cholate 0.10% 97 SDS 0.05% 98 DAC 0.05% 102
※Residual activity was measured by 4AA-DEA method
4AA, 4-Aminoantipyrine; DEA, Diethylaniline
Ac,CH3CO; PCMB, p-Chloromercuribenzoate; MIA, Monoiodoacetate; NEM, N-Ethylmaleimide; IAA, Iodoacetamide;
EDTA, Ethylenediaminetetraacetate; SDS, Sodium dodecyl sulfate; DAC, Dimethylbenzylalkylammonium chloride.
-
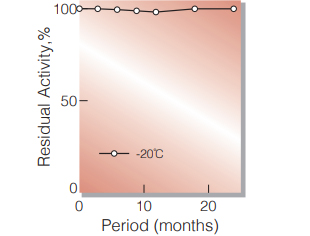
Fig.1. Stability (PEO-131)
(Powder form)(kept under dry conditions)
-
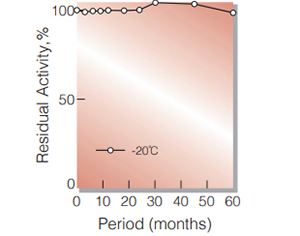
Fig.2. Stability (PEO-301)
(Powder form)(kept under dry conditions)
-
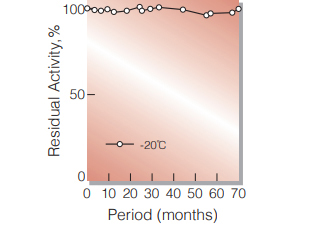
Fig.3. Stability (PEO-302)
(Powder form)(kept under dry conditions)
-
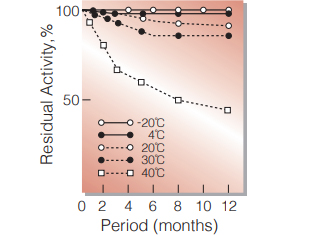
Fig.4. Stability (Powder form)
(kept under dry conditions)
-
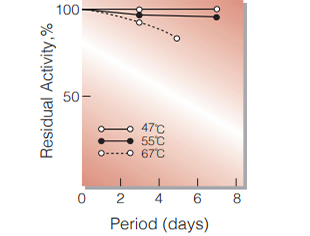
Fig.5. Stability (Powder form)
(kept under dry conditions)
-
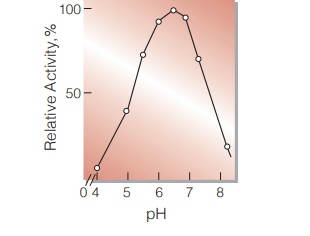
Fig.6. pH-Activity
20℃, 20sec-reaction in 0.1M buffer solution: pH4.0-6.0, acetate; pH6.0-8.0, phosphate
-
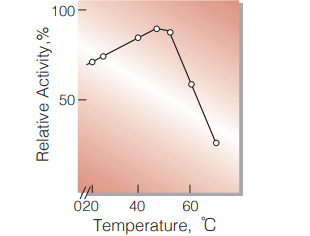
Fig.7. Temperature activity
20sec-reaction in 0.1M phosphate buffer, pH6.0
-
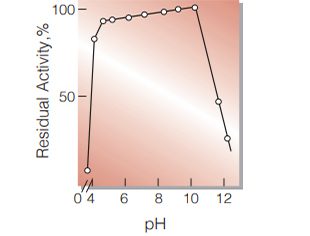
Fig.8. pH-Stability
25℃, 20hr-treatment with 50mM buffer solution: pH3.5-6.0, acetate; pH6.0-8.0, phosphate; pH9.0-11.0 borate
-
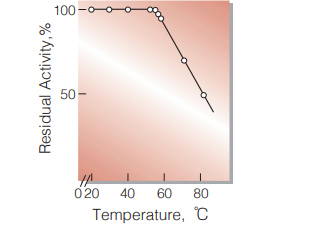
Fig.9. Thermal stability
10min-treatment with 50mM phosphate buffer, pH6.0
活性測定法(Japanese)
1. 原理

生成するPurpurogallinを405nmの吸光度の変化で測定する。
2.定義
上記反応原理のもと、20℃、pH6.0にて20秒間に1.0mgのPurpurogallinを生成する酵素量を1Purpurogallin単位(U)とする。
※下記条件下で測定した結果に係数を用いて上記の定義の単位に換算する。
3.試薬
- 過酸化水素希釈用緩衝液:
50mM リン酸緩衝液 pH6.4, 0.01%トリトンX-100含有 - 13.5mM 過酸化水素溶液(用時調整):
過酸化水素希釈用緩衝液 300mLに、30%(W/V)過酸化水素水0.459㎖を添加する。
- 7.8%(W/V) ピロガロール水溶液(用時調整)
- 酵素溶解・希釈用緩衝液:
0.1M リン酸緩衝液 pH6.0, 0.01%トリトンX-100含有
酵素溶液:酵素標品を予め氷冷したD液で分析直前に0.14~0.28U/㎖に希釈する。
4.手順
①C液の入った容器を37℃の恒温槽で予備加温しておく。
②試験管に下記溶液を混和し37℃で約3分間予備加温する。
| 4㎖ | B液 |
| 0.2㎖ | 酵素溶液 |
③予備加温後、C液を1.0mL添加して攪拌後、キュベット(d=1.0cm)に移し、水を対照に37℃に制御された分光光度計にセットする。
④C液添加後30秒後および90秒後の吸光度(405nm)を測定する。
ΔODtest=OD(90秒)-OD(30秒)
⑤盲検は、②で酵素溶液の代わりにD液を用いる。
ΔODblank=OD(90秒)-OD(30秒)
5.計算式
U/㎖ =(ΔODtest-ΔODblank)×0.473×希釈倍率
U/mg =U/㎖×1/C
| 0.473 | : 上記2. 定義のPurpurogallin単位(U)への換算係数 |
| C | : 溶解時の酵素濃度(C ㎎/㎖) |
| (注)1Purpurogallin単位は13.5国際単位(o-dianisidineを基質とし、25℃の反応条件下)に相当する。 | |
CONTACT
お問い合わせ-
各種製品に関するご質問・ご相談はこちらよりお問い合わせください。
