UAO-211
URICASE from Bacillus sp.
PREPARATION and SPECIFICATION
| Appearance | White amorphous powder, lyophilized | |
|---|---|---|
| Activity | GradeⅡ 1.5U/mg-solid or more | |
| Contaminants | Catalase | ≤1.0% |
| Stabilizers | Borate, EDTA, nonionic detergents | |
PROPERTIES
| Stability | Stable at −20℃ for at least one year (Fig.1) |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | approx.150,000 |
| Structure | 4 subunits per molecule |
| Isoelectric point | 4.7 |
| Michaelis constant | 1.36×10-5 M (Uric acid) |
| Inhibitors | Ag+,Hg++ |
| Optimum pH | 8.5 (Fig.4) |
| Optimum temperature | 45℃ (Fig.5) |
| pH Stability | pH 6.0−9.5 (25℃, 20hr) (Fig.6) |
| Thermal stability | below 60℃ (pH 8.0, 10min) (Fig.7) |
| Effect of various chemicals | (Table.1) |
APPLICATIONS
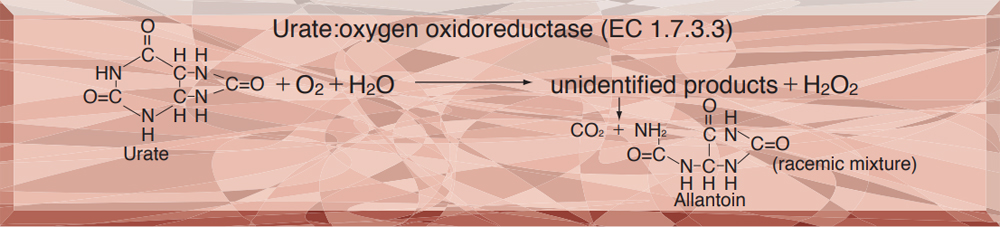
This enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of uric acid in clinical analysis.
ASSAY
Principle

The disappearance of uric acid is measured at 290nm by spectrophotometry.
Unit definition
One unit causes the oxidation of one micromole of uric acid per minute under the conditions described below.
Method
Reagents
| A. Uric acid solution | 0.001%[Dilute the stock solution (0.01%) to 10-fold volume with 50mM borate buffer containing 0.001% Triton X-100 and 1.0mM EDTA, pH 8.0](Should be prepared fresh) Stock solution : 10.0mg uric acid/100ml of above buffer (Store at 0−5℃) |
|---|---|
| B. KOH solution | 20% |
| C. Enzyme diluent | 50mM borate buffer containing 0.001% Triton X-100 and 1.0mM EDTA, pH 8.0 |
Procedure
1.Prepare the following reaction mixture in a test tube and equilibrate at 37℃ for about 5 minutes.
| 2.0ml | Uric acid solution | (A) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5ml | Distilled water |
| Concentration in assay mixture | |
|---|---|
| Borate buffer | 42 mM |
| Uric acid | 40 μM |
| EDTA | 0.83 mM |
| Triton X-100 | 0.00083% |
2.Add 0.5ml of the enzyme solution* and mix by gentle inversion.
3.After exactly 5 minutes at 37℃, add 0.2ml of 20% KOH solution (B) to stop the reaction and measure the optical density at 290nm against water (OD test).
At the same time, prepare the blank by first mixing the reaction mixture with 0.2ml of KOH solution after 5min-incubation at 37℃, followed by the addition of the enzyme solution (OD blank).
*Dissolve the enzyme preparation in ice-cold enzyme diluent (C) and dilute to 0.01−0.02U/ml with the same buffer and store on ice
Calculation
Activity can be calculated by using the following formula :
Volume activity (U/ml) =
-
ΔOD (OD blank−OD test)×Vt×df
12.2×1.0×t×Vs
= ΔOD×0.105×df
Weight activity (U/mg) = (U/ml)×1/C
| Vt | : Total volume (3.2ml) |
| Vs | : Sample volume (0.5ml) |
| 12.2 | : Millimolar extinction coefficient of uric acid (cm2/micromole) |
| t | : Reaction time (5 minutes) |
| 1.0 | : Light path length (cm) |
| df | : Dilution factor |
| C | : Enzyme concentration in dissolution (c mg/ml) |
REFERENCES
1) S.Asano, K.Yamamoto, S.Teshima, T.Kikuchi and Y.Kawamura; Rinsho Kagaku, 23 (3), 214 (1994)
2) K.Yamamoto, Y.Kojima, T.Kikuchi, T.Shigyo, K.Sugihara, M.Takashio and S.Emi; J.Biochem. 119, 80 (1996)
Table 1 Effect of Various Chemicals on Uricase
[This enzyme dissolved in 50mM borate buffer, pH 8.0 (5U/ml) was incubated with each chemical at 25℃ for 1hr.]
-
Chemical Concn.(mM) Residual
activity(%)None - 100 Metal salt 2.0 MgCl2 89 CaCl2 91 Ba(OAc)2 118 FeCl3 95 CoCl2 91 MnCl2 93 ZnSO4 91 Cd(OAc)2 87 NiCl2 89 CuSO2 78 Pb(OAc)2 91 AgNO3 44 HgCl2 46 PCMB 2.0 96 MIA 2.0 91 NaF 2.0 91 NaN3 2.0 91 -
Chemical Concn.(mM) Residual
activity(%)EDTA 5.0 104 o-Phenanthroline 2.0 91 α,α′-Dipyridyl 1.0 89 Borate 50 102 IAA 2.0 93 NEM 2.0 107 Hydroxylamine 2.0 91 2-Mercaptoethanol 2.0 104 Triton X-100 0.10% 93 Brij 35 0.10% 93 Tween 20 0.10% 98 Span 20 0.10% 103 Na-cholate 0.10% 98 SDS 0.05% 91 DAC 0.05% 89
Ac, CH3CO; PCMB, p-Chloromercuribenzoate; MIA, Monoiodoacetate; EDTA, Ethylenediaminetetraacetate;
IAA, Iodoacetamide; NEM, N-Ethylmaleimide; SDS, Sodium dodecyl sulfate; DAC, Dimethylbenzylalkylammonium chloride.
-
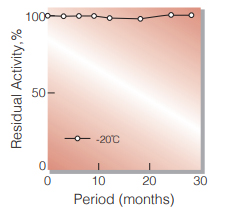
Fig.1. Stability (Powder form)
(kept under dry conditions)
-
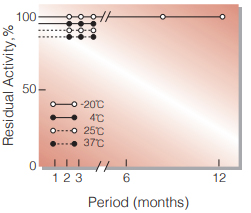
Fig.2. Stability (Powder form)
(kept under dry conditions)
-
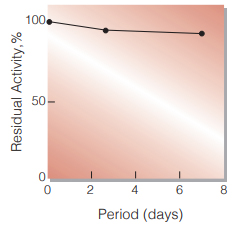
Fig.3. Stability (Liquid form)
(40℃,in GOOD's buffer solution pH7.0)
-
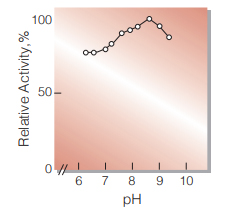
Fig.4. pH-Activity
(37℃,in 50mM borate buffer)
-
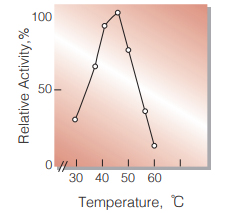
Fig.5. Temperature activity
5min-reaction in 50mM borate buffer, pH8.0
-
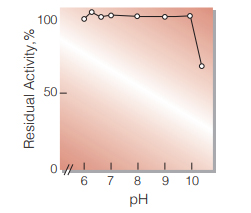
Fig.6. pH-Stability
25℃, 20hr-treatment with 50mM borate buffer
-
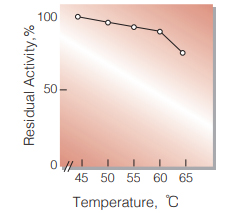
Fig.7. Thermal stability
10min-treatment with 50mM borate buffer, pH8.0
活性測定法(Japanese)
1. 原理

尿酸の消失量を290nmにおける吸光度の変化で測定する。
2.定義
下記条件下で1分間に1マイクロモルの尿酸を酸化する酵素量を1単位(U)とする。
3.試薬
- 0.001% 尿酸溶液 〔保存溶液(0.01%)を 0.001% Triton X-100及び1.0mM EDTAを含む 50mMホウ酸緩衝液,pH8.0で10倍希釈する〕(用時調製)保存溶液は10.0㎎の尿酸を同上緩衝液 100mlに溶解して調製する(0~5℃で保存)
- 20%KOH溶液
酵素溶液:酵素標品を予め氷冷した0.001%Triton X100および1.0mM EDTAを含む50mMホウ酸緩衝液,pH8.0で溶解し,同緩衝液で0.01 ~0.02U/mlに希釈し氷冷保存する。
4.手順
1.試験管に下記反応混液を調製し,37℃で約5分間予備加温する。
| 2.0ml | 尿酸溶液 | (A) |
| 0.5ml | 蒸留水 |
2.酵素溶液0.5mlを加え,反応を開始する。
3.37℃で正確に5分間反応させた後,KOH溶液(B)0.2ml を加えて反応を停止させる。この液につき290nmにおける吸光度を測定する(OD test)。
4.盲検は反応混液①を37℃で5分間放置後,KOH溶液 (B)0.2mlを加えて混和し,次いで酵素溶液0.5mlを加えて調製する。以下同様に吸光度を測定する(OD blank)。
5.計算式
U/ml =
-
ΔOD (OD blank−OD test)×3.2(ml)×希釈倍率
12.2×1.0×5(分)×0.5(ml)
| = ΔOD×0.105×希釈倍率 | |
| U/mg | = U/ml×1/C |
| 12.2 | : 尿酸のミリモル分子吸光係数 (cm2/micromole) |
| 1.0 | : 光路長(cm) |
| C | : 溶解時の酵素濃度(c mg/ml) |
CONTACT
お問い合わせ-
各種製品に関するご質問・ご相談はこちらよりお問い合わせください。
